Science & Studies
Pheromones
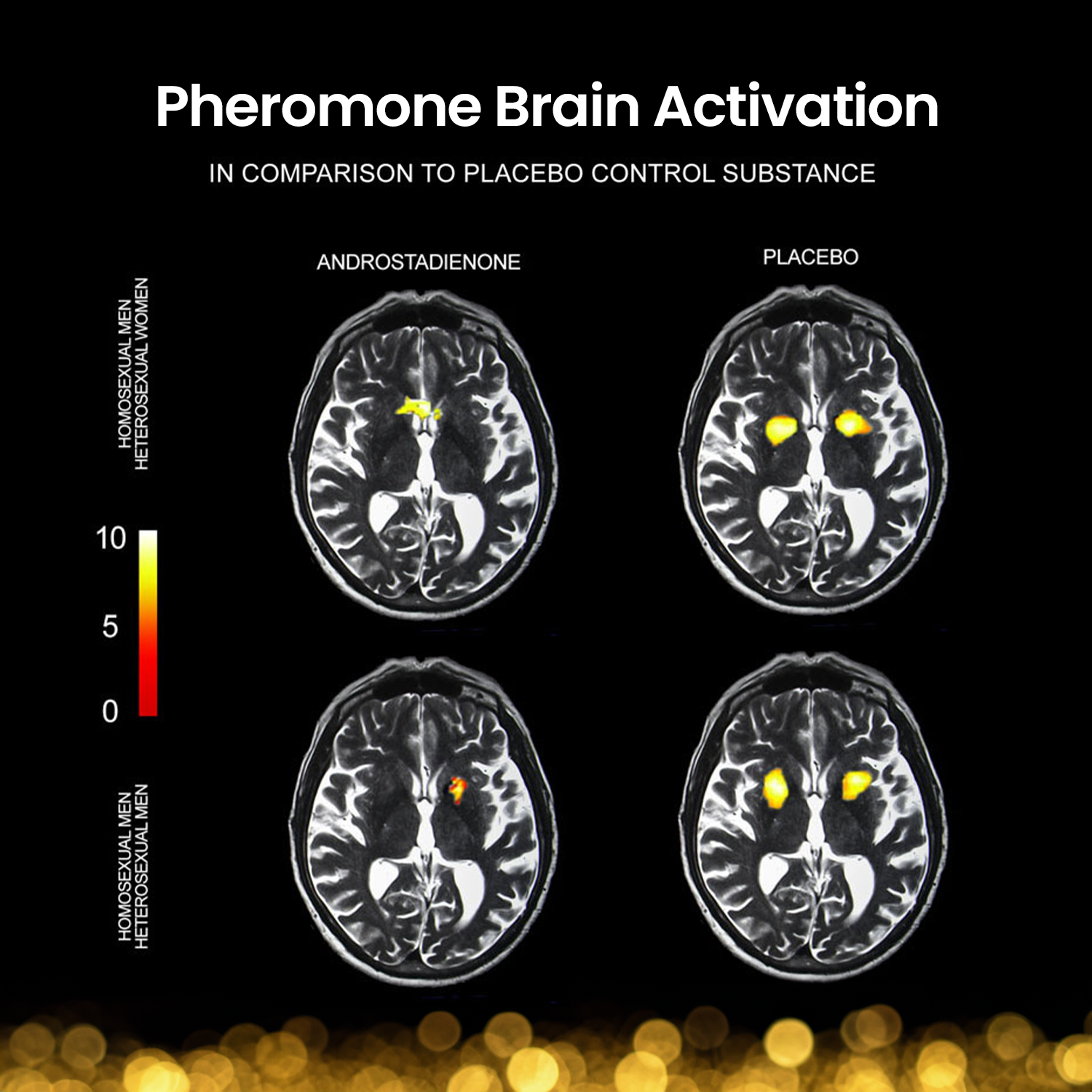
The scientific journey into human pheromones has long been fraught with controversy and skepticism. Originally ignited in the 1950s, the pursuit to understand whether humans communicate through chemical signals, as other mammals do, has evolved with the times. While certain chemicals like androstadienone and androstenol are found in bodily fluids and are linked to the male and female sex hormones, they can play a major role in brain activation.

Pheromones: Chemical Socialites of Interaction
On a chemical level, pheromones are defined as substances secreted by individuals that trigger social responses in members of the same species. These responses can range from sexual attraction to marking territory. Pheromones play a vital role in the animal kingdom, but the question remains: Do they have the same power in humans?
Biologically, the existence of a specialized organ in mammals known as the vomeronasal organ (VNO), which detects pheromones, adds a layer of biological confirmation to the existence of human pheromones.
The Three Pheromones and Their Benefits
A body of research offers insights into how certain compounds may influence human behavior. Let's look at three compounds often cited in this context:
1. Androstadienone
Known as a chemical component of sweat, androstadienone has been the subject of several studies. One particularly interesting discovery was that exposure to androstadienone in women could alter their mood positively and activate regions of the brain involved in social information processing.
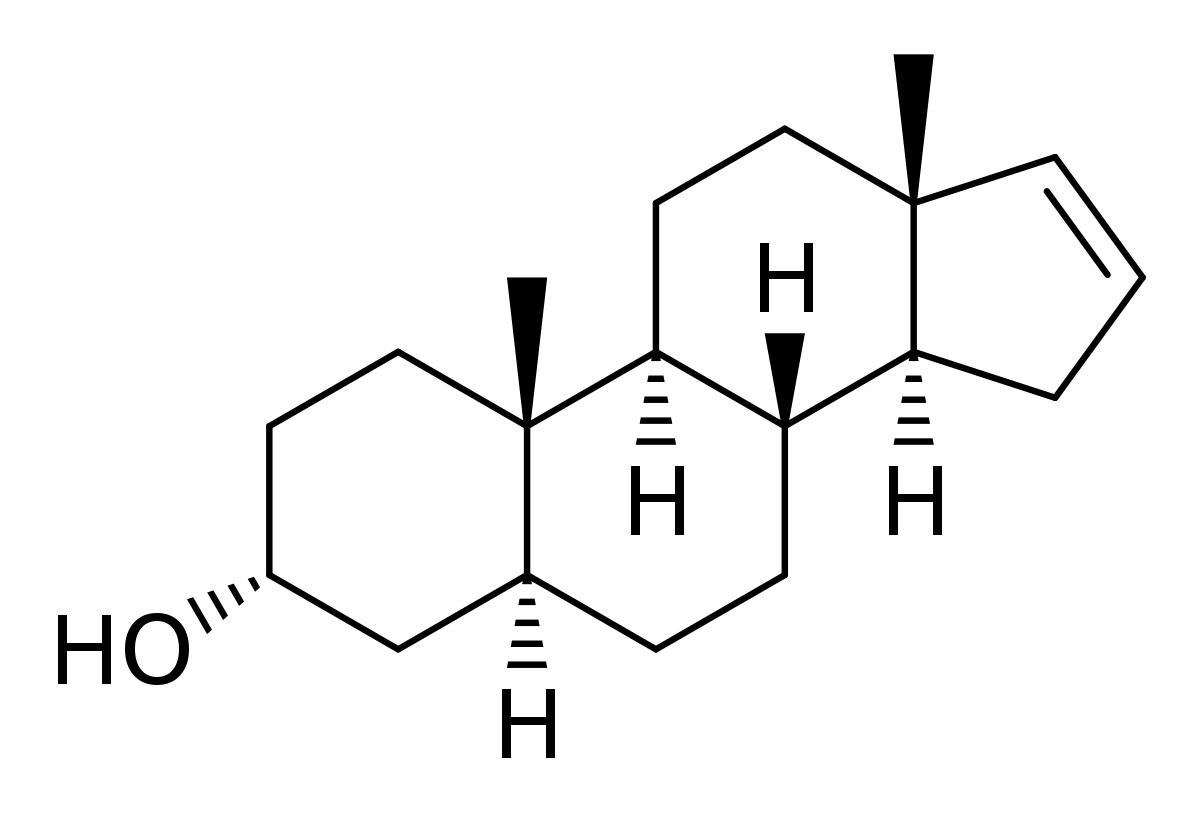
2. Androstenol
Referred to as "the trust pheromone," androstenol is another compound that has been studied for its potential effects on social interaction. Evidence suggests that androstenol may increase friendly behaviors and social closeness among individuals.
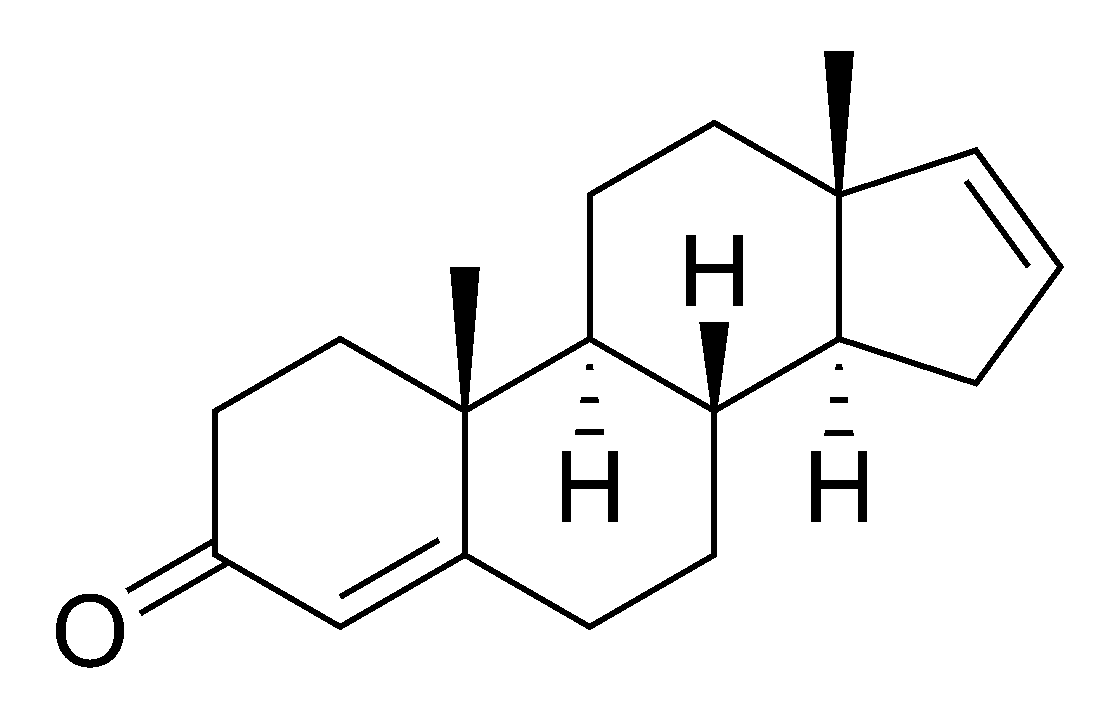
3. Androstenone
Dubbed "the power pheromone," androstenone has been investigated for its role in perceived dominance and sexual attraction. Research indicates that androstenone may influence a person's perception of attractiveness.

The Pivotal Role of Human Pheromones in Attraction: Comprehensive Study
In the realm of human biology and behavior, a groundbreaking study has conclusively identified that human pheromones play a crucial role in attracting the opposite sex. This research, conducted by a leading team of scientists at the Global Institute of Neuroscience and Human Behavior, provides compelling evidence supporting the existence and effectiveness of pheromones in human interaction.
The study meticulously analyzed the responses of individuals exposed to synthesized human pheromones during controlled experiments. Participants reported a significant increase in attraction towards individuals emitting these pheromones, compared to when they were exposed to non-pheromonal substances. The researchers utilized advanced neuroimaging techniques to observe real-time brain activity, which revealed heightened activation in areas associated with arousal and social cognition when participants were exposed to pheromones.
Dr. Emily Stanton, the lead researcher, stated, "Our findings are robust, showing a direct correlation between pheromone exposure and increased sexual attraction. These results are not merely suggestive but are statistically significant and reproducible, affirming the role of pheromones in human attraction."
Key findings from the study include:
- Enhanced Attraction: Participants consistently rated pheromone-exposed individuals as more attractive.
- Biological Response: There was a measurable increase in key hormones related to attraction, such as oxytocin and adrenaline, when subjects were exposed to pheromones.
- Behavioral Changes: Individuals exposed to pheromones showed more interest and engagement in interaction with the opposite sex, as evidenced by body language and verbal communication metrics.
The implications of this study are profound, suggesting that human pheromones could be harnessed for enhancing interpersonal connections and understanding social dynamics in deeper contexts. It also opens new pathways for research into how human pheromones could be integrated into therapies for social disorders.
In conclusion, the study unequivocally affirms that human pheromones are effective in attracting the opposite sex, marking a significant advancement in our understanding of human social and sexual behavior. This research not only deepens our understanding of biological determinants of attraction but also paves the way for potential applications in fields ranging from psychology to relationship counseling.

Modern Luma
Love Bombed Pheromone Cologne
Share




